Ovarian cancer
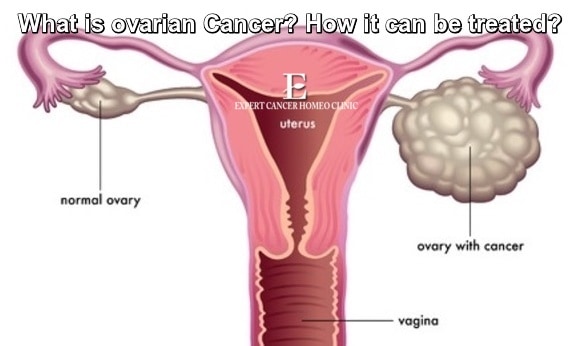
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the ovaries. Women have two ovaries, one on each side of the uterus. The ovaries — each about the size of an almond — produce eggs (ova) as well as the hormones estrogen and progesterone.
Ovarian cancer often goes undetected until it has spread within the pelvis and abdomen. At this late stage, ovarian cancer is more difficult to treat and is frequently fatal. Early-stage ovarian cancer, in which the disease is confined to the ovary, is more likely to be treated successfully.
Causes
It’s not clear what causes ovarian cancer.
In general, cancer begins when a genetic mutation turns normal cells into abnormal cancer cells. Cancer cells quickly multiply, forming a mass (tumor). They can invade nearby tissues and break off from an initial tumor to spread elsewhere in the body (metastasize).
Types of ovarian cancer
The type of cell where the cancer begins determines the type of ovarian cancer you have. Ovarian cancer types include:
- Epithelial tumors,which begin in the thin layer of tissue that covers the outside of the ovaries. About 90 percent of ovarian cancers are epithelial tumors.
- Stromal tumors,which begin in the ovarian tissue that contains hormone-producing cells. These tumors are usually diagnosed at an earlier stage than other ovarian tumors. About 7 percent of ovarian tumors are stromal.
- Germ cell tumors,which begin in the egg-producing cells. These rare ovarian cancers tend to occur in younger women.
Risk factors
Certain factors may increase your risk of ovarian cancer:
- Ovarian cancer can occur at any age but is most common in women ages 50 to 60 years.
- Inherited gene mutation.A small percentage of ovarian cancers are caused by an inherited gene mutation. The genes known to increase the risk of ovarian cancer are called breast cancer gene 1 (BRCA1) and breast cancer gene 2 (BRCA2). These genes were originally identified in families with multiple cases of breast cancer, which is how they got their names, but women with these mutations also have a significantly increased risk of ovarian cancer.
The gene mutations that cause Lynch syndrome, which is associated with colon cancer, also increase a woman’s risk of ovarian cancer.
- Estrogen hormone replacement therapy,especially with long-term use and in large doses.
- Age when menstruation started and ended.If you began menstruating before age 12 or underwent menopause after age 52, or both, your risk of ovarian cancer may be higher.
- Never being pregnant.
- Fertility treatment.
- Use of an intrauterine device.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
Symptoms
Early-stage ovarian cancer rarely causes any symptoms. Advanced-stage ovarian cancer may cause few and nonspecific symptoms that are often mistaken for more common benign conditions, such as constipation or irritable bowel.
Signs and symptoms of ovarian cancer may include:
- Abdominal bloating or swelling
- Quickly feeling full when eating
- Weight loss
- Discomfort in the pelvis area
- Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation
- A frequent need to urinate
Homoeopathic Treatment
The scope of Homeopathy for cancer management varies depending on the type of cancer, stage of cancer and the general health of the patient. Following are some of the aspects of Cancer management with Homeopathy:
- One of the most distressing complaints associated with some varieties of Cancer is the agonizing pain. Conventional medicines can provide pain relief but only to a certain extent and these medicines are not without any side effects. Moreover there is always a restriction to the dosage that can be safely administered to the patient. The advantage of administering Homeopathic medicines in such cases is that there can be effective pain control without inducing any side effects.
- Homeopathy can help in improving the general well being and vitality of the patient.
- Conventional treatment options for cancer (chemotherapy, radiotherapy, etc) are associated with distressing side effects and homeopathy can play a definitive role to counter these side effects.
- The diagnosis of cancer often leaves the patient with a sense of depression, anxiety and fear. The treatment may induce additional irritability, impatience and mood fluctuations. Homeopathy can influence the psyche of the patient and help him to deal with these emotions in a better way.
- Homeopathic medicines may also have a role to play in controlling the pace at which the disease increases and spread of the disease to other organs.
Homeopathic medicines can also be administered along with the allopathic medicines.